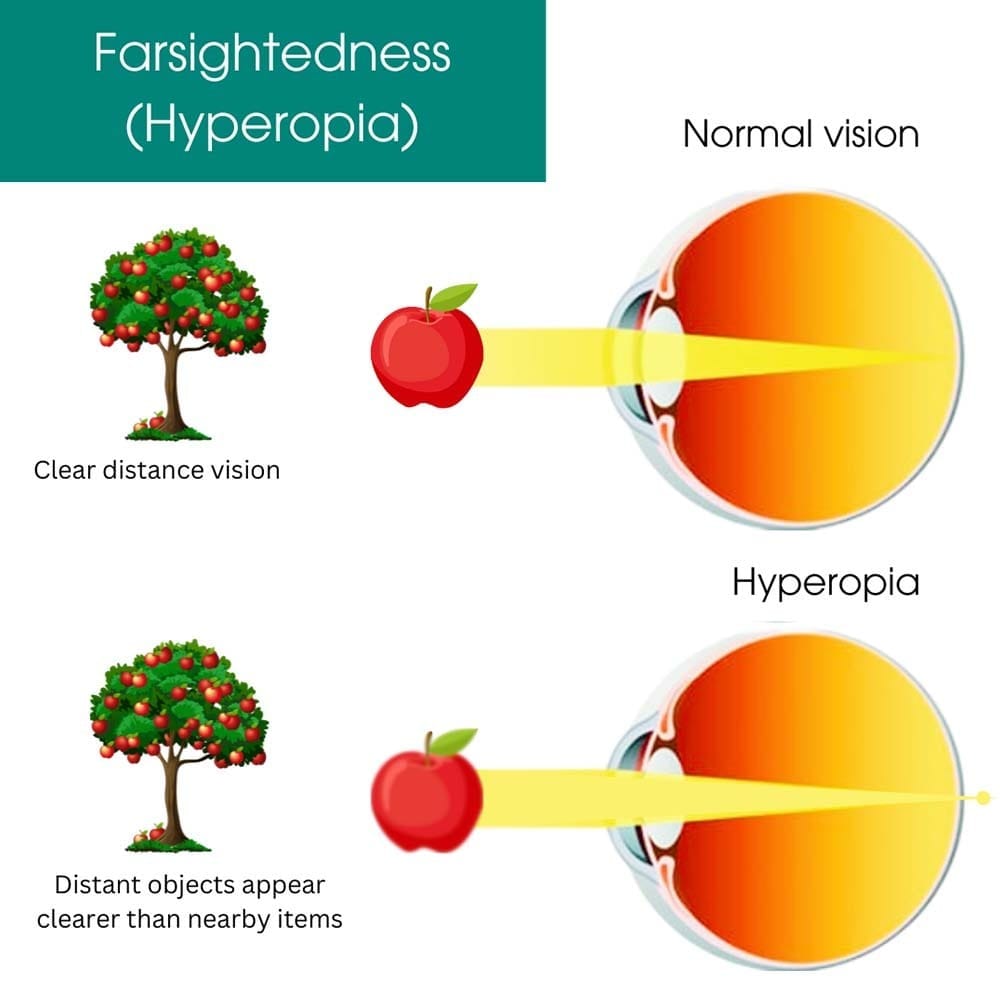
Farsightedness, also known as hyperopia, is a common vision problem in which distant objects appear clearer than nearby items. People with farsightedness may have difficulty reading or seeing items up close without glasses or contact lenses.
Hyperopia treatment depends entirely on how quickly you catch it. Quick intervention promises successful outcomes. With sufficient correction, such as glasses, contact lenses or refractive surgery, many people with farsightedness can achieve clear vision and effectively manage every visual activity. However, only an experienced optometrist can tell you what’s right for you because everyone is different.
Eye Physicians in New York City has several experienced eye specialists adept at diagnosing farsightedness and delivering the most effective treatment for hyperopia in Downtown Manhattan.
They offer eye treatments for a wide range of eye disorders, including:
Farsightedness is often observed in childhood, which is why it’s vital you have your children undergo a pediatric eye exam on a regular basis with a trained pediatric eye doctor like you find at Eye Physicians in NYC. Children may not be aware that they’re farsighted since their eyes can adapt to focus more effectively.
Depending on what’s causing it, it can be classified into various types including:
Each type causes clouded vision for close-up tasks. Farsightedness can range from mild to severe and is typically treated with eyeglasses, contact lenses or refractive surgery. It affects a large proportion of the population, with estimates ranging from five to 10 percent of Americans having moderate to severe farsightedness.
The severity and manifestations of symptoms differ from person to person; however, hyperopia often appears with common signs and symptoms such as:
Hyperopia symptoms in children vary slightly from those in adults. Early detection and intervention can help avoid possible vision problems from interfering with your child’s learning and development.
Some common symptoms in children include:
If you’re at high risk for certain eye diseases, such as glaucoma, schedule a dilated eye test every one to two years beginning at age 40. Untreated farsightedness can cause eyestrain, headaches and decreased visual function, limiting daily tasks such as reading and driving. It can cause amblyopia or strabismus in children, influencing learning and development.
A comprehensive eye examination is used to detect hyperopia. Snellen charts are used by optometrists and ophthalmologists to assess visual acuity. Refractive errors are measured using tools such as a phoropter or autorefractor. Eye health is evaluated through pupil dilation and retinal examination. Your eye doctor makes specific recommendations based on the results of these tests and your diagnosis determines which hyperopia treatment works best for your needs.
Corrective lenses, such as glasses or contact lenses, are commonly used to treat hyperopia. These lenses efficiently compensate for the refractive defect in hyperopia by altering how light rays reach the eye.
Other treatment options include:
Following refractive surgery such as LASIK or PRK, vision improves quickly, frequently within days, with the best outcomes in weeks. Recovery from refractive lens exchange is even faster, with significant improvement in one week and stabilization in several weeks. Ortho-K delivers clear daytime vision after the first night, but nightly lens use is required for maintenance.
If hyperopia, or farsightedness, goes untreated, it can cause chronic eyestrain, headaches and difficulties focusing on surrounding things. Over time, the eyes become more strained as they work harder to compensate for the refractive error, potentially causing visual problems and pain.
Untreated hyperopia also increases the likelihood of developing additional vision abnormalities, such as amblyopia or lazy eye or strabismus, another name for crossed eyes, especially in children. Your job opportunities may be reduced, and your quality of life suffers when you can’t participate in everyday activities.
Your eyes deserve the best care. Contact the experienced experts at Eye Physicians for full eye care and treatment. They are renowned for their professionalism and quick service, trying always to get you in and out of the office in less than an hour.
Eye Physicians
110 Lafayette St, Suite 503
New York, NY 10013
(212) 292-4814
Entrust the care of your precious eyesight to highly skilled and experienced eye care professionals. For top-notch ophthalmologists and optometrists in Downtown Manhattan, choose Eye Physicians. Eye Physicians ensures prompt care, precise diagnosis, and personalized treatment plans.
Schedule an Appointment